Risk management in investment is a critical aspect that can make or break investment success. From minimizing financial losses to maximizing returns, this topic delves into the strategies, types, and importance of managing risks effectively.
Importance of Risk Management in Investment

Risk management plays a crucial role in the world of investment, helping investors protect their capital and maximize returns. Without proper risk management strategies in place, investors are exposed to various uncertainties that can lead to significant financial losses.
Preventing Catastrophic Losses
Inadequate risk management can result in catastrophic losses for investors. For example, a lack of diversification in an investment portfolio can expose an investor to the risk of significant losses if a particular asset class underperforms or faces unexpected challenges. By implementing risk management techniques such as asset allocation and diversification, investors can mitigate the impact of such events and protect their capital.
Maximizing Returns and Capital Preservation
Effective risk management is not just about avoiding losses; it also plays a key role in maximizing returns. By carefully assessing and managing risks associated with different investment opportunities, investors can make informed decisions that balance risk and reward. This approach not only helps in preserving capital during market downturns but also allows investors to capitalize on opportunities for growth and wealth accumulation.
Regulatory Compliance
In the world of investment, regulatory compliance is essential to ensure that investors are protected and that financial markets operate efficiently. Risk management practices are often guided by regulatory requirements that aim to safeguard investor interests and maintain market integrity. By adhering to these regulations and implementing robust risk management frameworks, investors can navigate the complex landscape of investment with confidence and peace of mind.
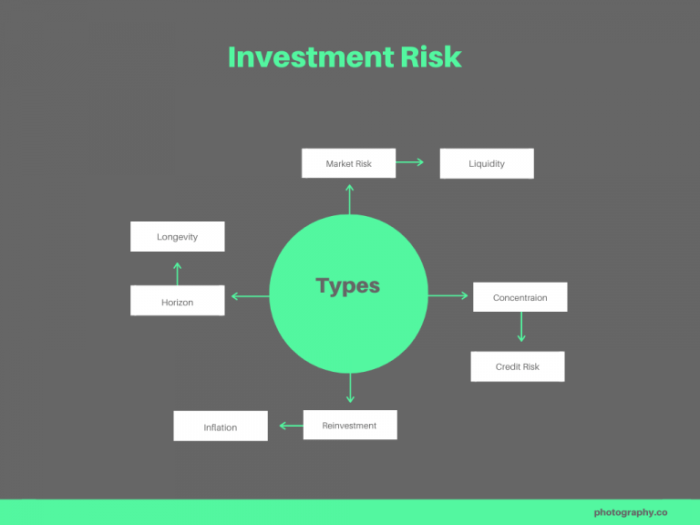
Types of Risks in Investment
When it comes to investing, there are various types of risks that investors need to consider. These risks can impact the performance of their investment portfolios and ultimately affect their financial goals. It is crucial for investors to understand the different types of risks they may face in order to make informed decisions and mitigate potential losses.
Systematic Risk, Risk management in investment
Systematic risk, also known as market risk, refers to the risks that are inherent in the overall market or economy. These risks cannot be diversified away and are beyond the control of individual investors. Factors such as interest rate changes, inflation, political instability, and natural disasters are examples of systematic risks. Systematic risks can impact all investments in the market, regardless of how well diversified a portfolio may be.
Unsystematic Risk
Unsystematic risk, also known as specific risk or diversifiable risk, is the risk that is specific to a particular company or industry. This type of risk can be reduced through diversification by investing in a variety of assets. Examples of unsystematic risks include company-specific events such as management changes, regulatory issues, or supply chain disruptions. By spreading investments across different assets, investors can minimize the impact of unsystematic risks on their overall portfolio.
How Each Type of Risk Impacts Investment Portfolios
Systematic risk affects the entire market and cannot be eliminated through diversification. Investors can only manage systematic risk through strategies such as asset allocation and hedging. On the other hand, unsystematic risk can be reduced through diversification, as it is specific to individual companies or industries. By spreading investments across different assets, investors can reduce the impact of unsystematic risks on their portfolio returns.
Strategies for Risk Management

Risk management is a crucial aspect of investment that involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to protect the capital invested. There are several common risk management strategies used in investment, including diversification and hedging.
Diversification
Diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, or geographic regions to reduce exposure to any single risk. By diversifying a portfolio, investors can potentially minimize the impact of adverse events on their overall investment performance. For example, instead of investing all funds in a single stock, an investor may choose to allocate funds across stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities to spread risk.
Hedging
Hedging is another risk management strategy that involves using financial instruments to offset the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. For instance, investors can use options contracts to hedge against potential losses in a stock position. By purchasing put options, investors can protect their downside risk in case the stock price declines. Similarly, futures contracts can be utilized to hedge against fluctuations in commodity prices.
Risk Assessment Techniques
In the realm of investment, risk assessment is a crucial process that helps investors evaluate the potential risks associated with their investment decisions. By systematically analyzing and quantifying risks, investors can make informed choices to protect their capital and maximize returns.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Risk Assessment Methods
When it comes to risk assessment techniques, investors can utilize both qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative risk assessment involves a subjective evaluation of risks based on factors such as industry trends, market conditions, and regulatory changes. On the other hand, quantitative risk assessment relies on numerical data and statistical models to quantify risks more precisely.
- Qualitative Risk Assessment:
- Relies on expert judgment and industry knowledge.
- Focuses on identifying and describing risks qualitatively.
- Uses techniques like risk matrices and risk registers.
- Quantitative Risk Assessment:
- Involves numerical data and statistical analysis.
- Utilizes tools like Value at Risk (VaR) to measure potential losses.
- Provides a quantitative estimate of the likelihood and impact of risks.
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical measure used to quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over a specific time frame. It helps investors understand the potential losses they could face under adverse market conditions.
Importance of Asset Allocation in Risk Management: Risk Management In Investment
Asset allocation plays a crucial role in managing investment risk by spreading out investments across different asset classes. This diversification helps reduce the impact of market fluctuations on the overall portfolio.
Significance of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation can help reduce portfolio volatility by balancing risk and return across different types of investments. By allocating assets strategically, investors can minimize the impact of losses in one asset class by gains in another, creating a more stable overall return.
- Diversification: By investing in a mix of asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, investors can spread risk and reduce the impact of volatility in any one market.
- Optimal Risk-Return Profile: Combining assets with different levels of risk and return potential can help investors achieve a balance that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Long-Term Growth: Asset allocation strategies that focus on long-term growth can help investors weather market cycles and achieve sustainable returns over time.
In conclusion, understanding risk management in investment is key to navigating the complex world of finance. By implementing sound strategies and acknowledging the various types of risks involved, investors can pave the way for a more secure and prosperous financial future.
Discover more by delving into High-return investment options further.